Volatility in Trading refers to the degree of price movement in a financial market over a given period. High volatility means prices are changing rapidly and unpredictably, while low volatility signals more stable and gradual price changes. Traders use volatility to assess risk and time their trades effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Volatility measures how much and how fast asset prices move.
- High volatility creates more trading opportunities but increases risk.
- It is affected by news, economic events, liquidity, and market sentiment.
- Traders use indicators like ATR, Bollinger Bands, and VIX to measure volatility.
- Managing risk is critical when trading in highly volatile markets.
Understanding Volatility in Financial Markets
Volatility is one of the most important concepts in trading. It helps traders evaluate risk, predict potential price swings, and adjust their strategies accordingly. Markets can be volatile due to news announcements, earnings reports, geopolitical events, or economic data releases.
Volatility can be categorized as:
- Historical Volatility: Based on past price movements.
- Implied Volatility: Based on market expectations of future price swings, commonly used in options trading.
What Causes Market Volatility?
Economic News and Reports
Announcements like GDP, inflation rates, employment data, and interest rate decisions often trigger large market reactions.
Political or Geopolitical Events
Elections, wars, or global conflicts can cause investor uncertainty, increasing volatility across global markets.
Liquidity
When there are fewer buyers and sellers in the market, prices can move more sharply, creating volatility even on low volume.
Market Sentiment
Fear and greed drive volatility. During times of panic or euphoria, price swings can be extreme.
High Volatility vs. Low Volatility
| Type | Characteristics | Best for |
| High Volatility | Large, unpredictable price swings | Day traders, scalpers |
| Low Volatility | Stable, slow price movements | Long-term investors, hedgers |
High volatility increases the potential for profit but also raises the risk of sudden losses. Low volatility offers fewer opportunities for short-term gains but is typically more predictable.
Measuring Volatility in Trading
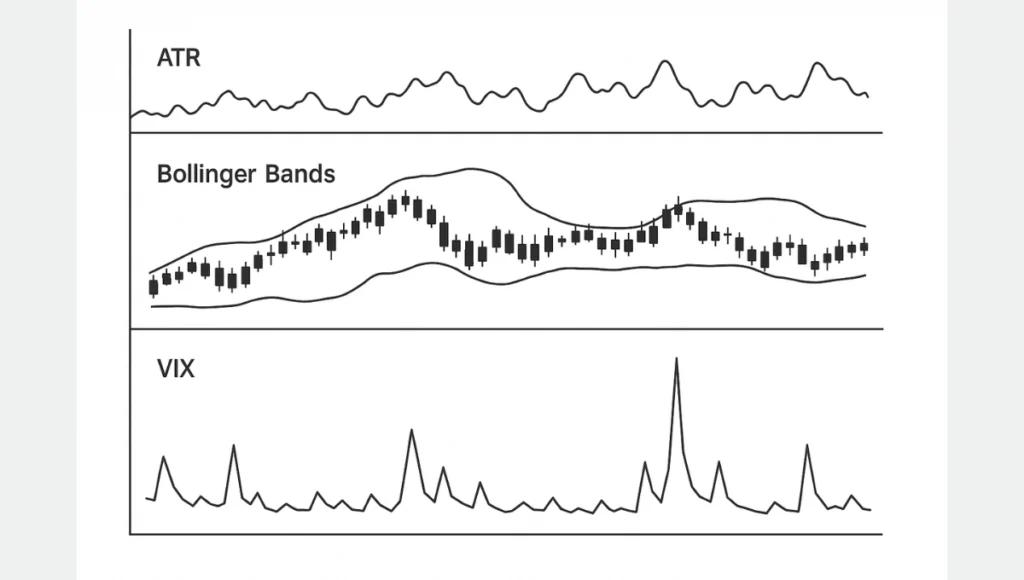
Traders use several tools and indicators to quantify volatility:
Average True Range (ATR)
ATR measures the average range between high and low prices over a set period. A rising ATR suggests increasing volatility.
Bollinger Bands
These bands expand and contract based on market volatility. Wider bands mean higher volatility, while narrower bands signal calm markets.
Volatility Index (VIX)
Known as the “fear index,” the VIX measures expected market volatility based on S&P 500 options. A high VIX means markets expect more movement.
Standard Deviation
Used in statistics and trading, this measures how far price data deviates from its average, helping to predict potential price fluctuations.
Volatility and Trading Strategies
Volatility Breakout Strategy
Traders look for the price to break above a resistance level or below a support level after a period of low volatility. The assumption is that volatility expansion will follow consolidation.
Range-Bound Strategy During Low Volatility
When markets are calm, traders often buy near support and sell near resistance within a tight price range.
News-Based Volatility Trading
Economic events like Fed announcements or nonfarm payroll data often cause temporary volatility spikes. Traders prepare by reducing position sizes or placing stop-loss orders.
Volatility in Different Asset Classes
Forex
The forex market is highly volatile due to leverage and global economic activity. Currencies like GBP, JPY, and exotic pairs tend to be more volatile than USD or EUR pairs.
Stocks
Small-cap and tech stocks often show higher volatility than large-cap blue-chip stocks. Earnings season increases volatility in stock prices.
Commodities
Gold, crude oil, and silver are highly sensitive to supply-demand changes, inflation expectations, and geopolitical news.
Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin, Ethereum, and altcoins are known for extreme volatility, often moving double-digit percentages in a single day.
Managing Risk in Volatile Markets
Volatility can create opportunities but also increases risk. Risk management is essential:
- Use smaller position sizes during high volatility.
- Place stop-loss and take-profit orders to lock in risk and reward.
- Avoid trading during news events if unprepared.
- Use volatility-adjusted position sizing to protect capital.
- Monitor leverage usage carefully.
Traders who survive volatile periods are those who manage risk better than others.
How Defcofx Helps Traders Handle Volatility
Master Market Volatility with Defcofx
Defcofx empowers traders with advanced tools and real-time data to confidently navigate volatile markets. Whether you’re trading forex, commodities, stocks, or crypto, our platform ensures you stay ahead of sudden market shifts.
Here’s what you get with Defcofx:
- Real-time volatility indicators across major asset classes.
- Educational content on tools like ATR, Bollinger Bands & VIX.
- Economic event calendars to anticipate high-impact news.
- Instant alerts for sudden market movements
- Smart risk tools to adjust leverage and position sizes in real time
Why Choose DefcoFX?
- High Leverage Options: Up to 1:2000 flexibility
- 40% Welcome Bonus: For first-time deposits of $1000 or more
- Zero Commissions & Swap Fees: Tight spreads from 0.3 pips
- Global Access: Open to clients worldwide with multilingual support
- Fast Support & Withdrawals: Funds processed within 4 business hours, even on weekends
Start trading smarter with Defcofx. Your partner for real-time volatility tracking and powerful trading advantages.
Open a Trading Live AccountFrequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Volatility is the measure of how much and how quickly prices move in the financial markets. High volatility means bigger, faster price swings.
It depends on your strategy. High volatility offers more opportunities for short-term trades but also increases the risk of losses.
You can use indicators like Average True Range (ATR), Bollinger Bands, and standard deviation. The VIX index also measures expected market volatility.
Economic news, geopolitical events, low liquidity, and changes in market sentiment can all increase volatility.
Reduce position sizes, use stop-loss orders, and avoid overleveraging. Always adjust your trading strategy based on current market volatility.
Yes, cryptocurrencies tend to be far more volatile than traditional stocks due to lower liquidity and rapid news cycles.
Yes, you can trade volatility indirectly through options, futures on the VIX, or ETFs that track volatility indexes.
Explore Other Forex Terms with Defcofx
Discover more forex glossary terms with Defcofx to help boost your knowledge as a beginner trader:

