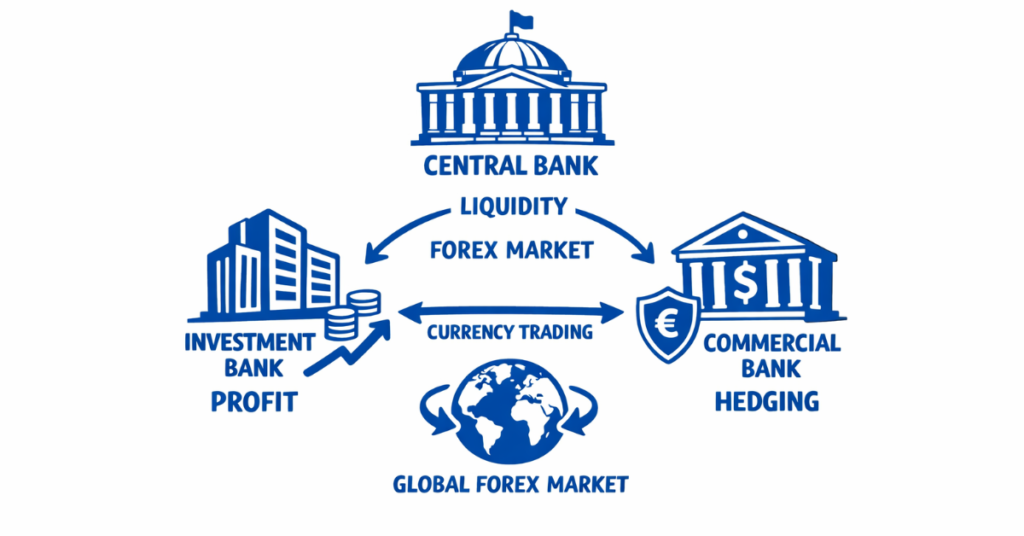
Yes, banks actively invest in forex to manage currency reserves, hedge risks, and profit from market fluctuations. Central banks stabilize national currencies, investment banks trade for profit, and commercial banks execute client orders. Understanding banks’ forex strategies helps retail traders make informed trading decisions.
Key Takeaways
- Banks invest in forex for profit, hedging, and liquidity management.
- Different types of banks participate differently: central, investment, and commercial banks.
- Banks influence market liquidity, spreads, and currency pricing.
- Retail traders can adopt strategies inspired by banks while managing risks responsibly.
What Is Forex Trading and How Banks Participate
Forex, or foreign exchange, is the global market where currencies are bought and sold. Banks are the largest participants, providing liquidity and executing massive trades that influence currency values. Central banks intervene to stabilize national economies, while investment and commercial banks trade for profit and client orders.
Types of Banks That Invest in Forex
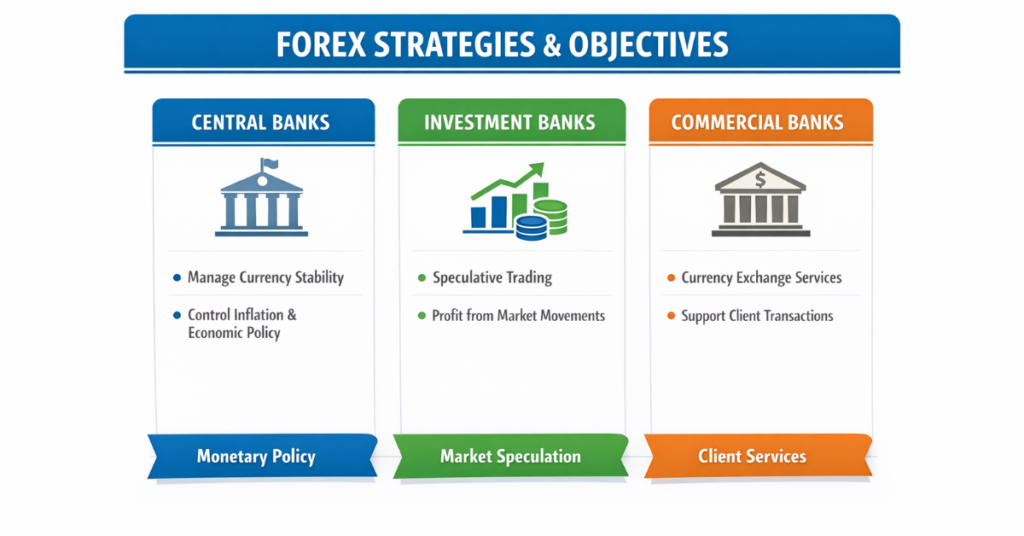
Banks participating in forex can be categorized into three main types:
1. Central Banks
Central banks, like the Federal Reserve or European Central Bank, trade forex primarily to manage national reserves, stabilize currency values, and control inflation. Their actions are policy-driven, not profit-focused.
2. Investment Banks
Investment banks engage in forex trading to generate profits, using proprietary strategies and speculative positions. They also provide market-making services for clients.
3. Commercial Banks
Commercial banks execute forex orders on behalf of clients, hedge their own exposures, and facilitate international trade transactions.
Why Banks Trade Forex
Banks trade forex for several key reasons that go beyond simple currency exchange. Profit generation is a primary goal for investment banks, which take advantage of currency fluctuations to earn significant returns. They employ advanced trading strategies, including algorithmic trading and hedging, to maximize gains while managing risk effectively.
Hedging is another critical reason. Banks often hold positions in multiple currencies to protect themselves and their clients from potential losses caused by sudden market movements. Commercial banks, in particular, use forex trading to manage the currency risk associated with international transactions, ensuring that businesses and clients can operate globally without exposure to unexpected losses.
Moreover, banks act as market makers, providing liquidity to the forex market. By continuously buying and selling currencies, they help maintain smooth market operations, narrow spreads, and facilitate high-volume trading for both institutional and retail participants.
How Banks Influence Forex Markets
Banks play a major role in shaping the forex market, both in terms of liquidity and pricing. Market liquidity refers to the ease with which currencies can be bought or sold without causing significant price changes. Banks, as the largest participants, provide this liquidity by executing large-volume trades that allow other traders to enter and exit positions smoothly.
By acting as market makers, banks set bids and ask prices for various currency pairs. Their trading activities directly affect spreads, which are the differences between buying and selling prices. When banks buy or sell large volumes, it can temporarily influence currency values, creating opportunities or risks for other traders.
Additionally, central banks can intervene to stabilize their national currency, often responding to economic or geopolitical events. Such interventions can impact exchange rates significantly, affecting global markets and retail trading conditions.
Comparison: Banks vs Retail Traders
Banks and retail traders operate in the same forex market, but their resources, strategies, and trading conditions differ significantly. Banks have access to high liquidity, advanced trading algorithms, and inside market information, allowing them to execute large trades with minimal market impact. Retail traders, on the other hand, trade smaller volumes and rely on public data, making them more susceptible to volatility.
Leverage and spreads are another key difference. While banks can utilize near-unlimited leverage internally, retail traders can access high leverage through brokers like Defcofx, which offers up to 1:2000 leverage, low spreads starting from 0.3 pips, and no commissions or swap fees, giving them a competitive edge in smaller-scale trading.
Banks also operate with a long-term strategic approach, using hedging to minimize risk, whereas retail traders often employ short-term strategies to capitalize on market movements. By studying banks’ methods, retail traders can adopt disciplined risk management techniques and informed decision-making.
How Retail Traders Can Learn From Banks
Retail traders can gain valuable insights by observing how banks approach forex trading. Banks prioritize risk management, research, and disciplined strategies, which are essential for consistent results. By adopting these principles, retail traders can reduce losses and improve decision-making.
Using advanced trading tools like MetaTrader 5 (MT5), traders can implement strategies similar to those used by institutional banks, including automated trading, technical analysis, and hedging techniques. Learning to analyze market trends, currency correlations, and economic indicators helps traders make informed choices rather than relying on speculation.
Retail traders can also benefit from choosing brokers that offer institutional-like conditions. For instance, Defcofx provides high leverage up to 1:2000, low spreads from 0.3 pips, fast withdrawals within 4 hours, and a 40% welcome bonus for first-time deposits, giving traders more flexibility to experiment and grow their accounts responsibly.
Final Thoughts on Do banks invest in forex?
Banks are significant players in the forex market, investing for profit, hedging, and providing liquidity. Central banks focus on stabilizing national currencies, while investment and commercial banks trade to maximize returns and facilitate client transactions. Understanding these strategies helps retail traders approach forex with greater insight and discipline.
Retail traders can learn from banks by adopting structured risk management, using research-driven strategies, and leveraging professional trading platforms. Brokers like Defcofx enable traders to access benefits such as high leverage up to 1:2000, low spreads from 0.3 pips, fast withdrawals within 4 hours, and a 40% welcome bonus, allowing them to trade more efficiently and with greater flexibility.
By studying institutional methods and applying them responsibly, retail traders can navigate the forex market more confidently while managing risks effectively.
Open a Live Trading AccountFAQs
No, not all banks trade forex. Central banks primarily intervene for economic stability, while investment and commercial banks trade actively for profit, client orders, and hedging purposes.
Retail traders cannot fully replicate banks due to differences in capital, access to liquidity, and information. However, they can adopt risk management strategies, research tools, and disciplined trading techniques to trade more effectively.
Central banks influence currency values by adjusting monetary policies, intervening in markets, and managing national reserves. Their actions can cause significant market volatility, affecting both institutional and retail traders.
Brokers like Defcofx provide high leverage up to 1:2000, low spreads starting from 0.3 pips, fast withdrawals within 4 hours, and a 40% welcome bonus, allowing retail traders to trade efficiently with flexible conditions.


