The intrinsic value of a stock is the true, underlying worth of a company’s shares based on fundamentals like earnings, cash flow, and growth potential, rather than its current market price. Investors use it to identify undervalued or overvalued stocks for informed decision-making.
Key Takeaways
- The intrinsic value helps determine whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued.
- Calculations can use methods like DCF, DDM, or Earnings Multiplier.
- Comparing intrinsic value with market price guides long-term investment decisions.
- Understanding intrinsic value reduces reliance on short-term market fluctuations.
What is the Intrinsic Value of a Stock?
The intrinsic value of a stock is the actual worth of a company’s shares based on its fundamental financial factors, including earnings, cash flow, growth potential, and risk. Unlike market price, which fluctuates due to supply, demand, and investor sentiment, intrinsic value reflects the stock’s true economic value. Understanding this value allows investors to make informed long-term investment decisions and identify stocks that are undervalued or overvalued.
Investors commonly use methods like Discounted Cash Flow (DCF), Dividend Discount Model (DDM), or the Earnings Multiplier Approach to calculate intrinsic value, ensuring investment choices are data-driven rather than speculative.
Why Intrinsic Value is Important for Investors
Understanding the intrinsic value of a stock is crucial for investors because it allows them to make data-driven decisions rather than relying on market hype or speculation. By knowing a stock’s true worth, investors can identify opportunities to buy undervalued stocks or sell overvalued ones, minimizing unnecessary losses and maximizing potential gains.
Traders using platforms like Defcofx can even leverage up to 1:2000, giving them the flexibility to capitalize on stocks that are priced below their intrinsic value. Combined with features like low spreads from 0.3 pips with no commissions or swap fees, this makes executing well-informed trades faster and more cost-efficient.
Intrinsic Value vs Market Value
The intrinsic value of a stock represents its true worth based on fundamentals like earnings, cash flow, growth potential, and risk, while the market value is simply the price at which the stock is currently trading on the exchange. Market value fluctuates constantly due to supply and demand, investor sentiment, news, and market trends, which may not reflect the company’s real economic value.
Investors compare intrinsic value with market value to identify trading opportunities. For instance, if a stock’s intrinsic value is $50 but its market price is $40, it may be considered undervalued, making it a potential buying opportunity. Conversely, if the market price is $60, the stock may be overvalued, signaling caution or a potential sell.
Using platforms like Defcofx, traders can leverage up to 1:2000, allowing them to act on undervalued stocks efficiently. Additionally, low spreads starting from 0.3 pips with no commissions or swap fees mean investors can enter positions without losing value to high trading costs. This combination of understanding value and using efficient trading tools can significantly improve decision-making and returns.
Methods to Calculate Intrinsic Value of a Stock
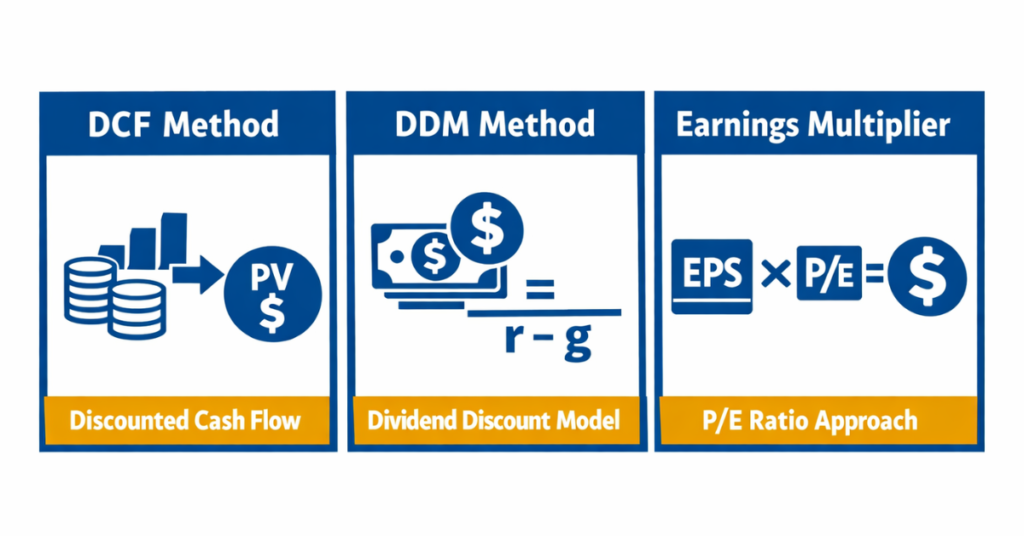
There are several widely used methods to calculate the intrinsic value of a stock, each relying on different financial factors to determine a company’s true worth. These methods help investors make informed decisions and spot potential opportunities.
1. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Method
This method calculates the present value of a company’s projected future cash flows. By discounting these cash flows at a rate reflecting the company’s risk, investors can estimate the stock’s intrinsic value. The DCF method is highly regarded for its accuracy in long-term valuation.
2. Dividend Discount Model (DDM)
The DDM focuses on companies that pay regular dividends. It calculates the present value of expected future dividends, considering dividend growth over time. This method is ideal for investors seeking stable, dividend-paying stocks.
3. Earnings Multiplier Approach
This approach multiplies a company’s expected earnings by a price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio adjusted for growth and risk factors. It provides a quick estimation of intrinsic value, particularly useful for comparative analysis across companies in the same sector.
Table: Methods, Formulas, and Pros/Cons
| Method | Formula | Pros | Cons |
| DCF | PV of Future Cash Flows | Accurate for long-term valuation | Sensitive to assumptions |
| DDM | PV of Future Dividends | Great for dividend stocks | Not suitable for non-dividend stocks |
| Earnings Multiplier | Earnings × Adjusted P/E | Quick comparison across companies | Less precise, oversimplified |
Platforms like Defcofx allow investors to use these valuation methods efficiently, while benefiting from high leverage up to 1:2000, fast withdrawals within 4 hours, and low-cost trading with no commissions or swap fees, making it easier to act quickly on undervalued stocks identified through intrinsic value analysis.
Open a Live Trading AccountStep-by-Step Calculation Example
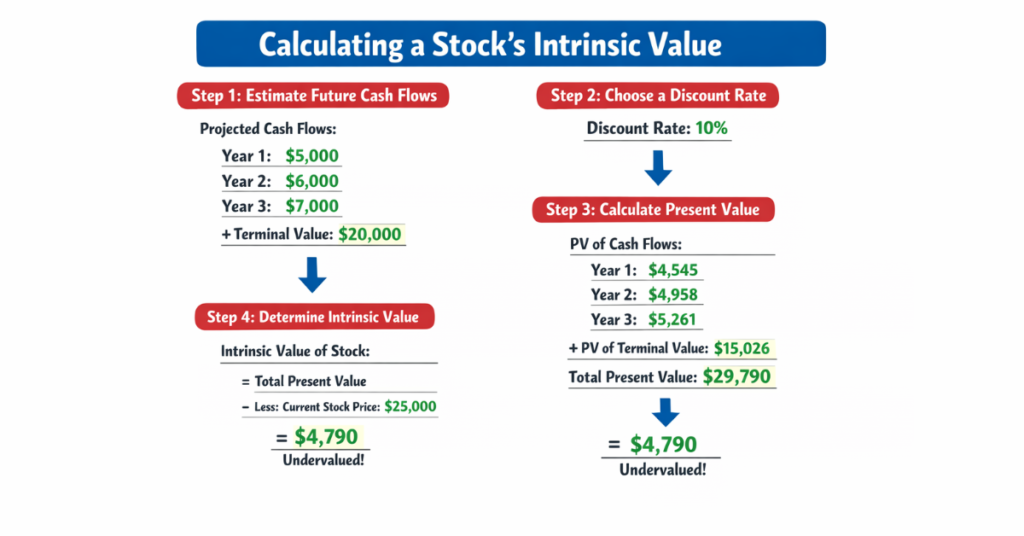
Let’s calculate the intrinsic value of a stock using the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) method as an example:
Step 1: Estimate Future Cash Flows
Assume a company is expected to generate the following free cash flows over the next five years:
- Year 1: $100,000
- Year 2: $120,000
- Year 3: $140,000
- Year 4: $160,000
- Year 5: $180,000
Step 2: Determine Discount Rate
Assume a discount rate of 10% to reflect the risk of the investment.
Step 3: Calculate Present Value of Each Cash Flow
Each future cash flow is discounted back to its present value using the formula:
PV = Future Cash Flow ÷ (1 + Discount Rate) ^ Year
Step 4: Sum All Present Values
Adding all discounted cash flows gives the total intrinsic value of the company.
Step 5: Divide by Number of Shares
Finally, divide the total intrinsic value by the total number of shares to get the intrinsic value per share.
5 Common Mistakes to Avoid When Calculating Intrinsic Value
Calculating the intrinsic value of a stock requires precision and careful analysis. Many investors make mistakes that can lead to overestimating or underestimating a stock’s true worth.
1. Ignoring Growth Rates: Failing to accurately estimate future earnings or cash flow growth can distort intrinsic value. Always use realistic, conservative growth projections.
2. Overestimating Earnings or Cash Flows: Assuming overly optimistic earnings without considering market trends or risks can result in inflated valuations, leading to poor investment decisions.
3. Using Incorrect Discount Rates: Applying a discount rate that doesn’t reflect the company’s risk level can make the stock appear more or less valuable than it truly is.
4. Relying Solely on One Method: Using only DCF, DDM, or Earnings Multiplier may overlook important factors. Combining multiple valuation methods provides a more accurate picture.
5. Ignoring Market and Industry Trends: Even if intrinsic value is calculated correctly, external factors like economic conditions or sector changes can impact stock performance.
Intrinsic Value Investing Strategy
An intrinsic value investing strategy focuses on buying stocks that are priced below their true worth and selling those that are overvalued. This approach helps investors make long-term, data-driven decisions instead of reacting to short-term market fluctuations.
Investors begin by calculating the intrinsic value of a stock using methods like DCF, DDM, or Earnings Multiplier. They then compare this value with the stock’s current market price to identify opportunities. Stocks trading significantly below intrinsic value are considered potential buys, while those trading above intrinsic value may be candidates for selling or avoiding.
Identify undervalued stocks with high growth potential.
Reduce the risk of overpaying for a stock.
Integrate valuation with market trends for better decision-making.
Advantages and Limitations of Intrinsic Value Analysis
Understanding the intrinsic value of a stock provides investors with a structured approach to evaluate investments, but it also has limitations that must be considered.
Table: Advantages vs Limitations
| Advantages | Limitations |
| Helps identify undervalued or overvalued stocks | Relies on assumptions that may be inaccurate |
| Reduces emotional or speculative trading | Requires detailed financial data and analysis |
| Supports long-term investment strategies | Market factors can cause short-term deviations |
| Facilitates better risk management | Different valuation methods may yield different results |
| Encourages disciplined investment decisions | Time-consuming and may be complex for beginners |
Final Thoughts on Intrinsic Value of a Stock
The intrinsic value of a stock is a vital metric that helps investors distinguish between undervalued and overvalued stocks, make informed long-term decisions, and minimize speculative risks. By combining intrinsic value analysis with careful market observation, traders can improve their investment strategies and identify profitable opportunities.
Open a Live Trading AccountFAQ’s
The intrinsic value can be calculated using methods like Discounted Cash Flow (DCF), Dividend Discount Model (DDM), or Earnings Multiplier Approach. Each method evaluates future earnings, cash flows, or dividends and discounts them to present value.
Intrinsic value reflects the stock’s true worth based on fundamentals, while market value is the current trading price, influenced by supply, demand, and investor sentiment.
Yes. As a company’s earnings, cash flows, growth prospects, and risk profile change, the intrinsic value also changes. Regular reassessment is important for accurate valuation.
Intrinsic value investing helps reduce speculative risks by focusing on fundamentals. However, it does not guarantee profits and market conditions can still affect outcomes.
Yes. Platforms like Defcofx provide advanced trading tools, calculators, and data access to assist investors in calculating intrinsic value efficiently, along with features like high leverage up to 1:2000 and low-cost trading with no commissions or swap fees.
Intrinsic value is best suited for long-term investing. Short-term trading relies more on market trends and technical indicators, while intrinsic value focuses on a stock’s fundamental worth.


