Momentum trading is a short- to medium-term strategy that buys assets showing strong price momentum and sells those losing it, using indicators like RSI, MACD, moving averages and volume to time entries and exits. It aims to capture directional moves while prioritizing strict risk management.
Key takeaways
- Momentum trading captures strong, continuing price moves rather than predicting reversals.
- Top indicators: RSI, MACD, EMA/SMA and volume (use them together for confirmation).
- Common setups: breakouts, moving-average crosses, and volume-surge entries.
- Works well in liquid, volatile markets (Forex, indices, some stocks).
- Proper stop-loss, position sizing and exit rules are essential, leverage amplifies both gains and losses.
- Broker features (execution speed, tight spreads, and accessible leverage) materially affect momentum outcomes.
What Is Momentum Trading?
Momentum trading is a market strategy where traders aim to profit from the continuation of existing price trends. The idea is simple: assets that are rising tend to keep rising for a while, and those falling often continue to drop until momentum fades. Traders use this approach to enter positions aligned with the prevailing trend rather than trying to predict reversals.
Momentum trading relies on speed, timing, and confirmation. It’s not about guessing tops or bottoms but about identifying strong movements backed by volume and market sentiment. Successful momentum traders know when to ride a move and when to exit before it reverses.
The stronger the momentum, the more likely the trend will persist until signs of exhaustion appear.
Momentum trading works particularly well in volatile, liquid markets such as Forex, indices, and commodities, where trends form quickly and opportunities arise frequently.
How Momentum Trading Works
Momentum trading works on the principle that strong price movements attract more traders, which further fuels the trend. This self-reinforcing loop continues until the momentum weakens, usually signaled by volume drops or exhaustion indicators.
Step-by-Step Breakdown
- Identify Momentum – Traders scan for assets showing strong price direction and volume spikes.
- Confirm the Trend – Indicators like RSI, MACD, or moving averages confirm that momentum is genuine and not just short-term volatility.
- Enter the Trade – Once momentum is validated, traders open a position in the direction of the move.
- Monitor and Adjust – Momentum traders constantly track market strength, tightening stops as the trend continues.
- Exit Strategically – When indicators show weakening momentum (e.g., RSI divergence, lower volume), traders close the trade before reversal.
Psychology Behind Momentum
Momentum trading thrives on market sentiment and herd behavior. When investors see prices moving quickly in one direction, they often join the trend, adding to its strength. Skilled traders exploit this behavior by entering early and exiting before emotions shift.
Momentum Trading Indicators
Momentum traders rely heavily on technical indicators to confirm the strength and direction of price moves. These tools help filter out false signals and identify the best moments to enter or exit trades. Below are the most commonly used momentum indicators and how they work together.
1. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The RSI measures how fast and how far prices have moved over a specific period (usually 14 days).
- Overbought zone (above 70): signals potential slowing of upward momentum.
- Oversold zone (below 30): indicates potential recovery or reversal.
- Used to confirm if current momentum still has strength or is fading.
2. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
The MACD tracks momentum shifts using two moving averages.
- A bullish signal appears when the MACD line crosses above the signal line.
- A bearish signal forms when it crosses below.
- Helps traders spot early trend changes and momentum acceleration.
3. Exponential & Simple Moving Averages (EMA/SMA)
These averages smooth out price fluctuations and highlight the underlying trend.
- A short-term EMA crossing above a long-term EMA signals strong bullish momentum.
- A cross below signals weakening or reversing momentum.
- Works best when combined with RSI or MACD for confirmation.
4. Volume Indicators
Volume measures trading activity and participation. A price rise backed by increasing volume shows true momentum strength.
- Indicators like On-Balance Volume (OBV) or Volume Oscillator confirm trend conviction.
- Declining volume during a move may warn of an upcoming reversal.
Popular Momentum Trading Strategies
Momentum trading can be applied in various ways depending on the trader’s style, risk tolerance, and timeframe. Below are the most effective momentum trading strategies that blend technical precision with real-time market psychology.
1. Breakout Strategy
Traders enter a position when the price breaks above resistance or below support with strong volume confirmation.
- The idea: once price escapes a key level, momentum continues in that direction.
- Ideal for trending markets with clear structure.
- Confirmation tools: Volume spike + MACD crossover.
Example: If EUR/USD breaks above 1.1000 with strong volume and RSI rising, a momentum trader might enter long, expecting further upward continuation.
2. Moving Average Cross Strategy
This approach uses two moving averages, one short-term (fast) and one long-term (slow).
- A bullish signal forms when the short-term MA crosses above the long-term MA.
- A bearish signal appears when it crosses below.
- Works well on higher timeframes (H1, H4, Daily) to avoid market noise.
Best tools: EMA 20 & EMA 50 cross paired with RSI > 50 for confirmation.
3. Volume Surge Strategy
Momentum without volume is weak. This strategy relies on identifying sharp increases in trading volume as a trigger for entry.
- Watch for candles with long bodies and high volume.
- The stronger the volume, the more likely momentum will sustain.
4. Momentum Reversal Strategy
This counter-momentum approach anticipates when a strong move is losing steam.
- Look for RSI divergence (price makes higher highs, RSI doesn’t).
- Confirm with MACD flattening or volume drop.
- Early exit or reversal trades can protect profits or capture turning points.
5. Combined Strategy Example
Many traders mix multiple signals for confirmation:
- Use RSI + MACD to spot momentum.
- Wait for a breakout with volume confirmation.
- Manage risk using stop-loss under the breakout level.
Momentum Trading in Forex Markets
Momentum trading is particularly powerful in the Forex market, where liquidity, volatility, and continuous price movement create ideal conditions for rapid trend shifts. Currencies often react strongly to macroeconomic news, giving traders numerous opportunities to capture short- and medium-term momentum moves.
1. Why Momentum Trading Fits Forex
The Forex market operates 24/5 with constant global participation, a natural environment for momentum.
- High liquidity: Ensures smooth execution and minimal slippage.
- Frequent volatility: News, rate decisions, and global events drive sharp trends.
- Multiple timeframes: Momentum setups appear from 1-minute charts to weekly swings.
2. Key Momentum Drivers in Forex
Momentum in currency pairs is influenced by:
- Economic reports: GDP, CPI, and NFP results can rapidly change sentiment.
- Central bank actions: Interest rate decisions or statements create strong directional pushes.
- Market sentiment: Safe-haven flows, geopolitical risks, and dollar strength all affect speed and duration of trends.
3. Using Momentum Indicators in Forex
Momentum traders in Forex rely heavily on RSI, MACD, and EMA crossovers:
- RSI identifies overbought/oversold zones during trending phases.
- MACD highlights changing momentum between bullish and bearish phases.
- EMA 20 & EMA 50 crossovers help define short-term versus medium-term trend momentum.
4. Enhancing Forex Momentum Trades with Defcofx
Trading momentum in Forex requires both tight spreads and fast execution. areas where Defcofx excels.
- High Leverage Options (up to 1:2000): Enables greater flexibility in managing short-term trades.
- No Commissions or Swap Fees: Keeps costs low, especially for intraday traders.
- Fast Withdrawals: Profits are processed within 4 business hours, even on weekends.
Risk Management in Momentum Trading
Momentum trading can deliver strong returns, but it also carries high risk due to rapid market movements. Traders must focus on protecting capital as much as generating profit. Proper risk management ensures you stay consistent, even during volatile conditions.
1. Position Sizing & Leverage Control
Always define how much of your account to risk on each trade ideally no more than 1–2% per position.
- High leverage gives flexibility, but use it strategically.
- Avoid over-leveraging; it can amplify both gains and losses.
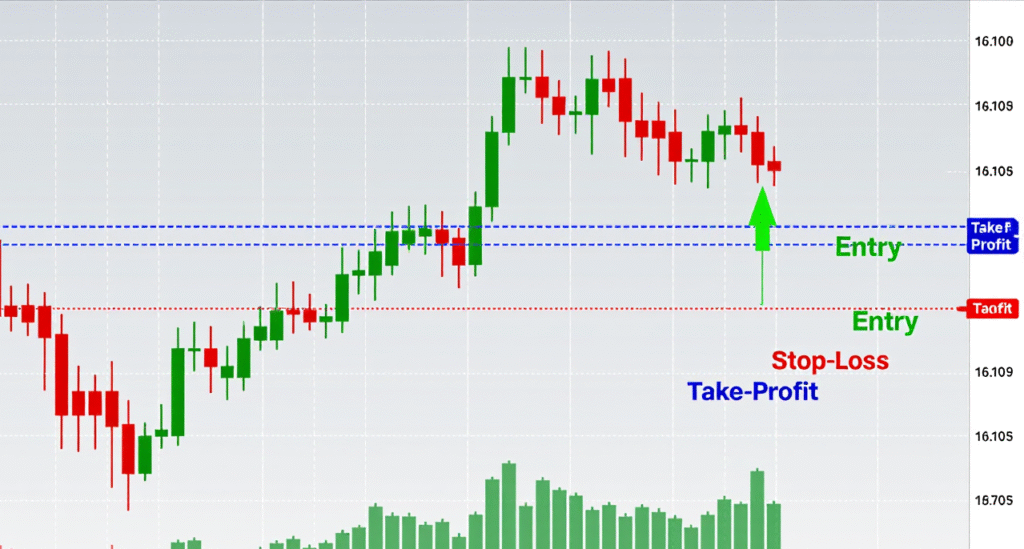
2. Setting Stop-Loss & Take-Profit Levels
Momentum can fade suddenly, that’s why clear exit rules are vital.
- Stop-loss: Place just beyond key support/resistance or recent swing points.
- Take-profit: Use a risk-to-reward ratio of at least 1:2 to maintain positive expectancy.
- Trail your stop to lock in profits as price moves in your favor.
3. Emotional Discipline
Momentum trading often triggers fear and greed due to fast price changes.
- Stick to your plan; avoid emotional entries after missing an initial move.
- Keep a trading journal to track mistakes and improve execution.
4. Diversifying Risk
Avoid putting all capital into one pair or asset. Spread your trades across multiple instruments or sessions.
- Diversify across Forex, commodities, and indices.
- Don’t trade correlated assets (e.g., EUR/USD and GBP/USD simultaneously).
Advantages and Disadvantages of Momentum Trading
Momentum trading can be one of the most rewarding yet challenging approaches in financial markets. Understanding its pros and cons helps traders use it effectively while managing its inherent volatility.
Advantages of Momentum Trading
1. High Profit Potential
Momentum trading capitalizes on strong, fast-moving price trends, allowing traders to earn significant profits in a short time frame.
- In volatile markets like Forex, these moves can last hours or even days.
2. Frequent Trading Opportunities
Momentum setups occur across all timeframes and assets, from major currency pairs to commodities.
- Traders can apply the same principles on intraday charts or long-term trends.
- Perfect for active traders who prefer dynamic markets.
3. Clear Entry and Exit Signals
Indicators like RSI, MACD, and Moving Averages provide structured confirmation for when to enter or exit a trade.
- This clarity reduces emotional decisions and supports rule-based trading.
4. Compatibility with Automated Systems
Because momentum strategies rely on indicators, they can easily be automated through trading bots or EAs (Expert Advisors).
- Automation ensures consistency and removes emotional bias.
Disadvantages of Momentum Trading
1. High Risk from Rapid Reversals
Momentum can fade suddenly after major news releases or large institutional profit-taking.
- Late entries often lead to losses when trends exhaust.
- Always use stop-loss and trailing stops for protection.
2. Requires Constant Monitoring
Momentum trades demand real-time tracking due to fast price fluctuations.
- Not ideal for traders who prefer passive investing or long-term holding.
3. Market Noise and False Signals
Short-term volatility may create fake breakouts or reversals that trigger premature entries.
- Combining multiple indicators and confirming with volume helps reduce false signals.
4. Psychological Pressure
The need for quick decisions can cause emotional fatigue. Maintaining mental discipline is essential for consistent results.
Final Thoughts on Momentum Trading
Momentum trading remains a powerful strategy for traders who seek to capitalize on strong, directional price movements rather than predicting reversals. By leveraging popular tools like RSI, MACD, EMAs, and volume indicators, traders can identify high-probability entries and ride the wave of market sentiment with precision. This approach works best in liquid, volatile markets such as forex and indices where momentum builds quickly and offers frequent opportunities for profits.
However, success in momentum trading demands strict risk management, emotional control, and constant market monitoring. Sudden reversals, news events, or diminishing volume can swiftly invalidate a setup, making stop-losses and predefined exit strategies essential. With the right blend of technical skill, disciplined execution, and trusted trading infrastructure, momentum traders can thrive in fast-moving markets while minimizing unnecessary risks.
(FAQs) About Momentum Trading
Momentum trading is a strategy where traders buy assets showing strong upward movement and sell those showing downward movement, aiming to profit from the continuation of price trends rather than predicting reversals.
The most reliable indicators include:
Relative Strength Index (RSI): detects overbought/oversold conditions.
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): confirms shifts in momentum.
Exponential Moving Averages (EMA): highlight trend direction and speed.
Volume indicators: confirm the strength behind price moves.
It can be but only with proper risk management. Beginners should start small, use demo accounts, and practice identifying valid momentum signals before trading live.
Momentum trading works across multiple markets, including:
Forex (high liquidity and volatility)
Commodities (like gold or oil)
Indices and stocks (during strong trends)
Use stop-loss orders to cap potential losses.
Avoid risking more than 1–2% of your capital per trade.
Employ trailing stops to secure profits as trends extend.
Defcofx Forex Articles You Shouldn’t Miss
Discover powerful forex strategies in these top reads from Defcofx.
- How to Turn $1000 Into $10000 in a Month?
- Best Currency Pairs to Trade During London Session
- How Much is 0.5 Lot Size in Dollars
- Best Time To Trade NZD/USD
- What Is Considered the Greatest Risk Associated With Forex Settlement?
- Is NZD/USD a Major or Minor Pair?
- Trailing Stop Limit: Definition, Uses & Trading Guide
- When Does a Bearish Market Become Bullish in Forex?
- Is Pound Stronger than Dollar?


